Understanding Bladder Cancer and Its Treatment Landscape
Bladder cancer typically begins in the cells lining the bladder and can either be non-muscle-invasive or muscle-invasive. Non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) accounts for approximately 70-75% of cases, while muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) is more aggressive and spreads deeper into the bladder wall and surrounding tissue.
Treatment Challenges in Bladder Cancer:
- Recurrence Rates: Non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer has high recurrence rates, requiring long-term follow-up.
- Resistance to Conventional Treatments: Muscle-invasive bladder cancer is more resistant to treatments like chemotherapy and radiation.
- Personalized Treatment: As every cancer is unique, treatments must be tailored to each patient's tumor characteristics.
1. Surgical Options for Bladder Cancer Treatment
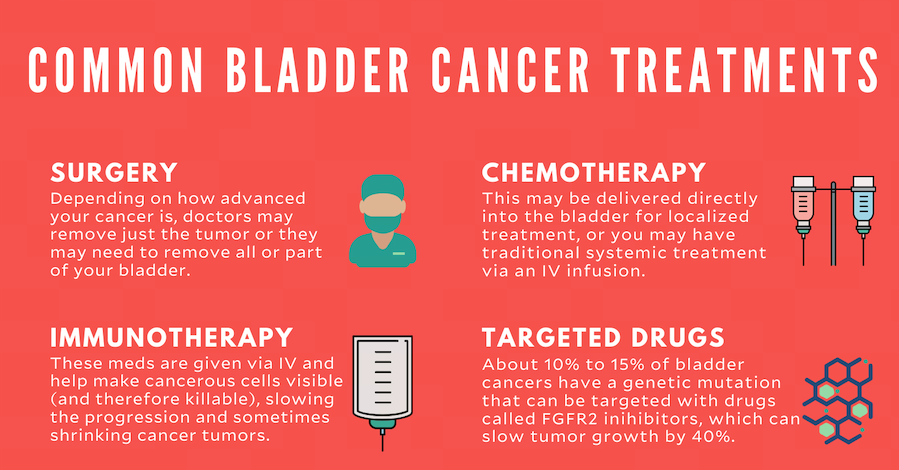
Surgery remains a cornerstone in the treatment of bladder cancer. Depending on the stage and type of bladder cancer, patients may undergo various surgical procedures. In 2025, surgical techniques will be more advanced, with improved outcomes and fewer side effects.
Types of Surgical Procedures:
- Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT): This is the most common procedure for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. It involves removing tumors from the bladder using a scope inserted through the urethra.
- Cystectomy: In cases of muscle-invasive bladder cancer, a radical cystectomy may be performed, where the entire bladder is removed. This may be combined with lymph node dissection to check for the spread of cancer.
- Robotic-Assisted Surgery: In 2025, robotic cystectomy and other minimally invasive techniques will become more widespread, leading to quicker recovery times, smaller incisions, and less blood loss.
Benefits of Surgical Treatment:
- Immediate Results: Surgery provides an immediate option for removing tumors, especially in localized bladder cancer.
- Increased Precision: Robotic-assisted surgeries offer greater precision, reducing complications and recovery time.
2. Chemotherapy: The Backbone of Bladder Cancer Treatment
Chemotherapy has long been used to treat bladder cancer, particularly in cases of muscle-invasive bladder cancer or for patients who are not candidates for surgery. In 2025, chemotherapy will likely be combined with other therapies to improve efficacy and reduce side effects.
Key Chemotherapy Drugs for Bladder Cancer:
- Cisplatin: A powerful drug used in combination with other chemotherapy agents to treat advanced bladder cancer.
- Carboplatin: An alternative for patients who cannot tolerate cisplatin.
- Gemcitabine: Often combined with cisplatin for better results in advanced-stage bladder cancer.
Benefits of Chemotherapy:
- Systemic Treatment: Chemotherapy can target cancer cells throughout the body, including those that may have spread from the bladder.
- Combination Therapy: Chemotherapy can be combined with other therapies, such as immunotherapy and targeted therapy, to enhance effectiveness.
3. Immunotherapy: A New Era in Bladder Cancer Treatment
Immunotherapy has emerged as a groundbreaking treatment for advanced bladder cancer in recent years, and its use is expected to expand significantly by 2025. Checkpoint inhibitors and other immunotherapeutic drugs are helping the body’s immune system recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively.
Types of Immunotherapy for Bladder Cancer:
- Checkpoint Inhibitors: Drugs like nivolumab (Opdivo) and pembrolizumab (Keytruda) block the proteins that prevent immune cells from attacking bladder cancer cells.
- BCG Therapy: Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) therapy is used to treat non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer by stimulating the immune system to attack cancer cells. By 2025, improved BCG formulations are expected to enhance its effectiveness.
- CAR T-Cell Therapy: Though still in clinical trials, CAR T-cell therapy could potentially offer a new, personalized treatment option for bladder cancer.
Benefits of Immunotherapy:
- Targeted Action: Immunotherapy focuses on enhancing the body’s immune system rather than attacking cancer cells directly, leading to fewer side effects.
- Long-Term Response: Many patients have shown durable responses to immunotherapy, leading to longer remission periods.
4. Targeted Therapy: Precision Treatment for Bladder Cancer
Targeted therapy is increasingly becoming a part of the treatment landscape for bladder cancer, especially for patients whose cancer has specific genetic mutations. By targeting these mutations, treatments can be more effective with fewer side effects than traditional chemotherapy.
Key Targeted Therapies for Bladder Cancer:
- FGFR Inhibitors: Fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) inhibitors, such as erdafitinib, target mutations in the FGFR pathway that contribute to cancer growth.
- HER2 Targeted Therapy: For patients with overexpression of the HER2 protein, drugs like trastuzumab (Herceptin) may be used to inhibit tumor growth.
Benefits of Targeted Therapy:
- Precision: These therapies target specific genetic mutations, leading to a more personalized and effective treatment.
- Fewer Side Effects: Unlike chemotherapy, targeted therapy works by attacking specific cancer cells, which reduces damage to normal, healthy cells.
Bladder Cancer Treatment Options Summary
| Treatment Type | Key Approaches/Drugs | Effectiveness | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surgery | TURBT, Radical Cystectomy, Robotic-Assisted Surgery | High for localized cancers, effective in removing tumors | Pain, infection, long recovery for major surgeries |
| Chemotherapy | Cisplatin, Carboplatin, Gemcitabine | Effective for advanced stages | Nausea, fatigue, hair loss |
| Immunotherapy | Checkpoint Inhibitors, BCG Therapy, CAR T-Cell | Effective for advanced cases, long-term responses | Fatigue, skin reactions, fever |
| Targeted Therapy | FGFR Inhibitors, HER2 Targeted Therapy | High for patients with specific mutations | Mild side effects, depending on drug |
With innovations in treatment options, bladder cancer is becoming more treatable, and patients have greater hope for a better future.
Bladder Cancer Treatment Options in 2025: What’s Next?
By 2025, we expect to see even more breakthroughs in the treatment of bladder cancer. The integration of personalized medicine, advanced genomic testing, and minimally invasive procedures will likely be standard practice.
What Patients Can Expect:
- More Combination Therapies: The future of bladder cancer treatment will focus on combining multiple treatment modalities, such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapies, to achieve better results.
- Fewer Side Effects: With innovations like robotic surgery and targeted treatments, patients will experience fewer side effects, making recovery easier and quicker.
- Improved Survival Rates: Thanks to ongoing research, bladder cancer survival rates will continue to rise as treatment becomes more effective and personalized.
Conclusion
Bladder cancer treatment options are rapidly evolving, providing patients with better, more personalized choices than ever before. By 2025, we can expect significant advancements in immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and minimally invasive techniques, all of which are helping to improve patient outcomes. Whether through cutting-edge surgery, new drug therapies, or innovative combinations of treatments, the future of bladder cancer treatment looks increasingly promising.