Why Choosing the Right Gas Sensor Matters
Gas sensors detect the presence and concentration of gases in the air, playing a vital role in:
- Workplace safety (e.g., detecting toxic or combustible gases)
- Environmental monitoring (air quality assessment)
- Process control (industrial automation)
- Smart homes and buildings (CO2 and VOC monitoring)
Selecting the appropriate sensor enhances safety, optimizes processes, and prevents costly false alarms or sensor failures.
Types of Gas Sensors Available in 2025
Choosing a gas sensor begins with understanding the sensor types and their operating principles:
1. Electrochemical Gas Sensors
- Function: Measure gas concentration via chemical reactions producing an electrical signal.
- Best for: Toxic gases like carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), and oxygen monitoring.
- Advantages: High sensitivity, low power consumption.
- Limitations: Limited lifespan, affected by humidity and temperature.
2. Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) Sensors
- Function: Detect gases by change in electrical resistance of a metal oxide layer.
- Best for: Combustible gases like methane, propane, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- Advantages: Durable, cost-effective, fast response.
- Limitations: Sensitive to humidity and temperature changes, moderate selectivity.
3. Infrared (IR) Gas Sensors
- Function: Use absorption of infrared light to detect gases like CO₂ and hydrocarbons.
- Best for: Combustible gases and CO₂ monitoring.
- Advantages: Long lifespan, unaffected by humidity.
- Limitations: Higher cost, bulky compared to other types.
4. Catalytic Bead Sensors
- Function: Detect combustible gases by oxidizing the gas on a heated bead.
- Best for: Detecting flammable gases in industrial environments.
- Advantages: Good for a wide range of combustible gases.
- Limitations: Requires oxygen presence, limited lifespan.
5. Photoionization Detectors (PIDs)
- Function: Ionize gases with ultraviolet light and measure current generated.
- Best for: Detecting VOCs and hazardous organic gases at low concentrations.
- Advantages: Highly sensitive.
- Limitations: Expensive and complex maintenance.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Gas Sensor
Selecting the right gas sensor depends on your specific requirements:
| Factor | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Target Gas | Identify the specific gas(es) you need to detect. |
| Detection Range | Ensure sensor sensitivity matches required detection limits. |
| Response Time | Faster response needed for safety-critical applications. |
| Operating Environment | Account for temperature, humidity, and potential contaminants. |
| Lifespan and Maintenance | Longer life and low maintenance reduce operational costs. |
| Power Consumption | Important for battery-powered or remote applications. |
| Size and Integration | Sensor dimensions and compatibility with your device/system. |
| Cost | Balance between performance and budget constraints. |
Popular Applications of Gas Sensors in 2025
Industrial Safety and Monitoring
Industries use gas sensors to detect leaks of toxic or explosive gases, ensuring worker safety and regulatory compliance.
Environmental and Air Quality Monitoring
Sensors monitor pollutants like CO₂, NOx, and VOCs in urban and indoor environments to improve health standards.
Smart Buildings and HVAC Systems
Gas sensors integrated into HVAC systems optimize ventilation by monitoring CO₂ levels and indoor air quality.
Automotive Industry
Monitoring exhaust gases and cabin air quality for safety and regulatory standards.
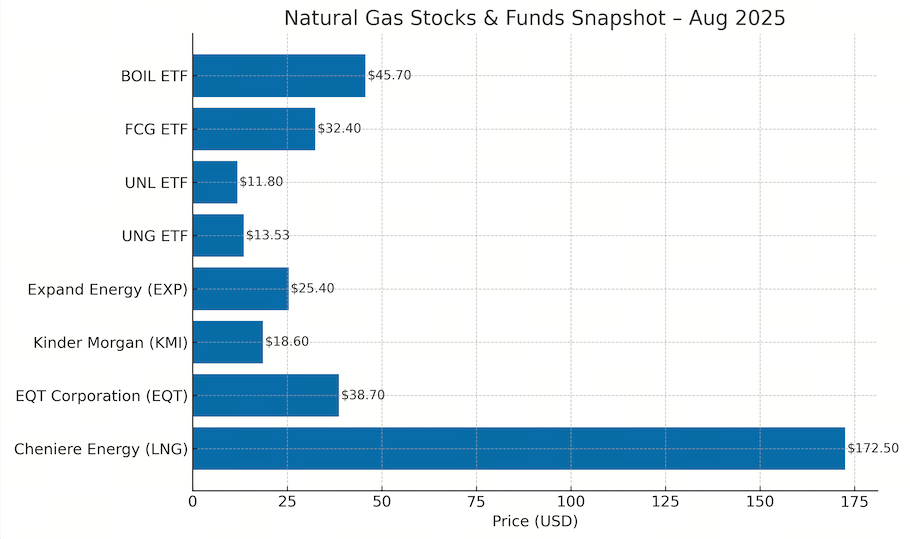
Gas Sensor Selection Chart for Common Gases
| Gas | Recommended Sensor Type | Typical Application | Response Time | Operating Environment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Monoxide (CO) | Electrochemical | Indoor air quality, industrial | Seconds | Variable temperature/humidity |
| Methane (CH₄) | MOS, Catalytic Bead, IR | Leak detection, refinery safety | Seconds | Harsh industrial environments |
| Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) | Infrared (NDIR) | HVAC, environmental monitoring | Seconds | Indoor/outdoor |
| Hydrogen Sulfide (H₂S) | Electrochemical | Wastewater, oil & gas | Seconds | Harsh, corrosive environments |
| VOCs | Photoionization Detector (PID), MOS | Environmental and industrial | Seconds | Variable |
Tips for Implementing Gas Sensors Successfully
- Calibrate sensors regularly to maintain accuracy.
- Use multi-sensor arrays for better selectivity in complex environments.
- Incorporate sensor diagnostics to monitor sensor health.
- Choose sensors with certifications (e.g., UL, ATEX) for safety-critical applications.
- Ensure compatibility with your monitoring or control systems.
Final Thoughts: Make Informed Gas Sensor Choices in 2025
The right gas sensor choice is crucial for safety, efficiency, and regulatory compliance across many industries in the US. By understanding sensor types, key features, and application needs, you can select a solution that provides accurate, reliable, and timely gas detection.
Stay ahead in 2025 by investing in modern, trusted gas sensors tailored to your environment and operational demands.