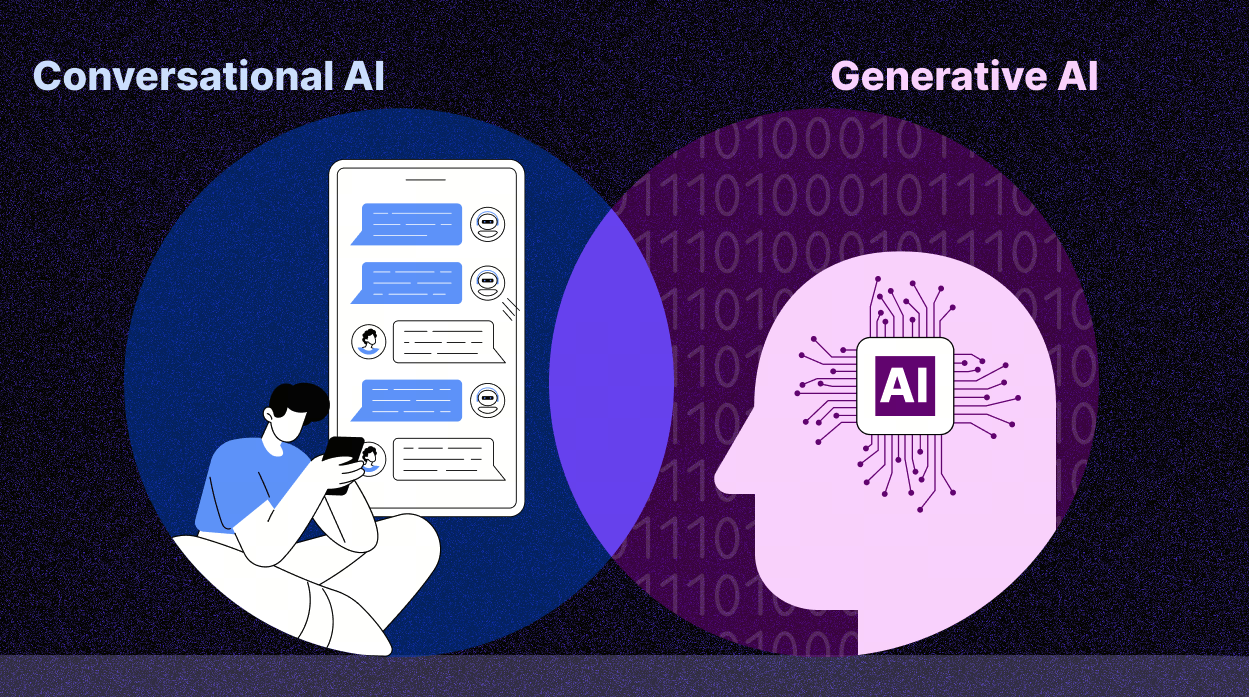
What is Conversational AI?
Conversational AI refers to technologies that enable machines to understand, process, and respond to human language in a way that mimics natural conversation. These systems rely on Natural Language Processing (NLP) and machine learning to interact with users via text or voice interfaces. Common examples include chatbots, virtual assistants, and customer service applications.
Key Features of Conversational AI:
- Real-time interactions: Handles conversations and provides instant feedback.
- Task-oriented: Focuses on answering specific questions or completing tasks.
- Multimodal: Can operate through both voice and text channels.
Examples of Conversational AI:
- Siri: Apple's voice-activated assistant.
- Alexa: Amazon's virtual assistant that helps with various tasks.
- Chatbots: Used by businesses for customer support on websites and social media.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI refers to AI systems designed to generate new, original content based on input data. Unlike Conversational AI, which is often focused on understanding and responding, Generative AI is about creating new content, including images, text, music, and even code. These systems are powered by deep learning models, including Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and transformer models, like GPT-3.
Key Features of Generative AI:
- Content creation: Can generate new, unique content based on training data.
- Unsupervised learning: Often learns patterns from large datasets without specific task guidance.
- Highly creative: Produces outputs like text, images, and even entire articles.
Examples of Generative AI:
- GPT-3: A language model by OpenAI capable of generating human-like text.
- DALL·E: An AI that generates images from textual descriptions.
- Deepfake: AI-generated videos that manipulate human appearance or behavior.
Conversational AI vs Generative AI: Key Differences
The main difference between Conversational AI and Generative AI lies in their goals and capabilities. Let's break them down:
| Aspect | Conversational AI | Generative AI |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Facilitates human-like interaction and communication | Creates new content (text, images, music, etc.) |
| Primary Technology | Natural Language Processing (NLP), machine learning | Deep learning, GANs, transformer models |
| Functionality | Task-oriented, answering questions or completing tasks | Creative, producing original content |
| Examples | Chatbots, voice assistants, customer support AI | GPT-3, DALL·E, Deepfake, AI music generators |
Use Cases for Conversational AI
Conversational AI is best suited for situations where real-time interaction with users is required. Some common use cases include:
- Customer Support: Chatbots can provide instant responses to common queries, improving customer satisfaction.
- Virtual Assistants: Voice assistants like Google Assistant or Siri help users with daily tasks, like setting reminders or sending messages.
- E-commerce: AI-powered chatbots guide users through online shopping, recommend products, and handle transactions.
Use Cases for Generative AI
On the other hand, Generative AI excels in scenarios where creating new, unique content is the focus. Some key use cases include:
- Content Creation: Platforms like GPT-3 are used to generate articles, blogs, and even poetry.
- Image Generation: Tools like DALL·E create detailed, high-quality images based on textual prompts.
- Entertainment: Generative AI creates music, video content, and even generates synthetic voices for entertainment purposes.
Benefits of Conversational AI
- Improved User Experience: Provides real-time assistance and engages users in a natural, conversational manner.
- Automation: Helps businesses automate repetitive tasks, reducing workload and increasing efficiency.
- 24/7 Availability: Chatbots and virtual assistants are available around the clock, ensuring constant support.
Benefits of Generative AI
- Enhanced Creativity: Generates original content that can inspire human creativity, from art to writing.
- Speed: AI can generate content quickly, saving time in processes like content creation or coding.
- Cost-Effective: Reduces the need for human labor in content creation, lowering production costs.
Limitations of Conversational AI
While Conversational AI offers numerous benefits, it does come with some limitations:
- Limited Understanding: Can struggle with complex queries or contexts that require deep understanding.
- Task-Oriented: Not capable of generating creative or unique content.
- Dependence on Data: Its performance depends on high-quality data and ongoing training.
Limitations of Generative AI
Similarly, Generative AI faces certain challenges:
- Quality Control: AI-generated content may sometimes lack accuracy or quality.
- Ethical Concerns: The potential misuse of deepfake technology and AI-generated content raises ethical questions.
- High Computational Costs: Training generative models requires significant computing resources.
Conclusion
Both Conversational AI and Generative AI represent major advancements in artificial intelligence, with distinct applications and capabilities. Conversational AI shines in interactive, real-time environments where efficiency and task completion are key. In contrast, Generative AI excels in creating new, innovative content across various media.
As these technologies continue to evolve, their integration into various industries will significantly impact how we communicate, create, and consume content. Whether you're looking for an AI-driven assistant to help with daily tasks or an AI tool to generate original works of art, understanding the differences between Conversational AI and Generative AI is key to leveraging their full potential in 2025.